Abstract
Research Article
Vestibular-limbic relationships: Brain mapping
Paolo Gamba*
Published: 16 March, 2018 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 007-013
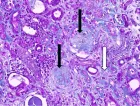
Vestibular disorders and anxiety are closely related, probably because they share some neuronal pathways. Ageing and patient comorbidities are important facilitating factors, and multiple vascular risk factors could contribute to the onset of a vestibular syndrome called vascular vertigo. White matter lesions (WML) are often seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of elderly people and are related to various geriatric disorders, including dizziness. The cause of this correlation could be the disruption of neuronal networks that mediate higher vestibular cortical function. Numerous neuronal pathways link the vestibular network with limbic structures and the prefrontal cortex modulates anxiety through its connections to amygdala. The aim of the present work was to investigate the correlation between WML, amygdala and cognitive functions.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001006 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Amygdala; White matter lesions; Chronic subjective dizziness; Anxiety
References
- Brandt T, Strupp M, Dieterich M. Towards a concept of disorders of "higher vestibular function". Front Integr Neurosci. 2014; 8: 47. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Fy1fNX
- Teggi R, Caldirola D, Perna G, Bellodi L, Bussi M. Vestibular testing in patient with panic disorders and chronic dizziness. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2007; 27: 243-247. Ref.: https://goo.gl/grZHWL
- Simon NM, Pollack MH, Tuby KS, Stern TA. Dizziness and panic disorders: a review of the association between vestibular dysfunction and anxiety. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1998; 10: 75-80. Ref.: https://goo.gl/F6gPwp
- Lindgren A, Roijer A, Rudling O, Norrving B, Larsson EM, et al. Cerebral lesions on magnetic resonance imaging, heart disease, and vascular risk factors in subjects without stroke. A population-based study. Stroke. 1994; 25: 929-934. Ref.: https://goo.gl/tJKA85
- Manolio TA, Kronmal RA, Burke GL, Poirier V, O'Leary DH, et al. Magnetic resonance abnormalities and cardiovascular disease in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke. 1994; 25: 318-327. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VoxUqq
- Longstreth WT Jr., Manolio TA, Arnold A, Burke GL, Bryan N, et al. Clinical correlates of white matter findings on cranial magnetic resonance imaging of 3301 elderly people. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke. 1996; 27: 1274-1282. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2qiko2
- Liao D, Cooper L, Cai J, Toole J, Bryan N, et al. The prevalence and severity of white matter lesions, their relationship with age, ethnicity, gender, and cardiovascular disease risk factors: the ARIC Study. Neuroepidemiology. 1997; 16: 149-162. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GbSaHB
- Guidetti G. The role of cognitive processes in vestibular disorders. Hearing, Balance and Communication. 2013; 11: 3-35. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7GMKNy
- Monzani D, Casolari L, Guidetti G, Rigatelli M. Psychological distress and disability in patient with vertigo. J Psychosom Res. 2001; 50: 319-323. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XbhjoH
- Carmeli E. Anxiety in the Elderly Can be a Vestibular Problem. Front Public Health. 2015; 3: 216. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1EQyie
- Colledge N, Lewis S, Mead G, Sellar R, Wardlaw J, et al. Magnetic resonance brain imaging in people with dizziness: a comparison with non-dizzy people. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002; 72: 587-589. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vGgknW
- Gufoni M, Guidetti G, Nuti D, Pagnini P, Vicini C, et al. The relationship between cognitive impairment, anxiety-depression symptoms and balance and spatial orientation complaints in the elderly. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2005; 25: 12-21. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JTDqMe
- Guidetti G. La terapia della vertigine vascolare nella pratica ambulatoriale: esperienza multicentrica (Studio VascVert). Otorinolaringol. 2005; 55: 237-246.
- Maillard P, Fletcher E, Harvey D, Carmichael O, Reed B, et al. White matter hyperintensity penumbra. Stroke. 2011; 42: 1917-1922. Ref.: https://goo.gl/j1EDn6
- Kim KW, MacFall JR, Payne ME. Classification of white matter lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in elderly persons. Biol Psychiatry. 2008; 15: 273-280. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QDQDcm
- Ruckenstein MJ, Staab JP. Chronic Subjective Dizziness. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2009; 42: 71-77. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5B3z4p
- Ott A, Breteler MM, van Harskamp F, Stijnen T, Hofman A. Incidence and risk of dementia. The Rotterdam study. Am J Epidemiol. 1998; 147: 574-580. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ceq4Uf
- Vermeer SE, Prins ND, den Heijer T, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, et al. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348: 1215-1222. Ref.: https://goo.gl/TpVogx
- Matsusue E, Sugihara S, Fujii S, Ohama E, Kinoshita T, et al. White matter changes in elderly people: MR-pathologic correlations. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2006; 5: 99-104. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wHg1Mk
- de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Bots ML, Witteman JC, Oudkerk M, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis and cerebral white matter lesions in a population based magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurol. 2000; 247: 291-296. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fUkPZU
- Debette S, Markus HS. The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2010; 341: c3666. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Qp2RGN
- Benisty S, Gouw AA, Porcher R, Madureira S, Hernandez K, et al. Location of lacunar infarcts correlates with cognition in a sample of non-disabled subjects with age-related white-matter changes: the LADIS study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80: 478-483. Ref.: https://goo.gl/S2SEsn
- Gong L, Liu XY, Fang M. Recent progress on small vessel disease with cognitive impairment. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8: 7701-7709. Ref.: https://goo.gl/e1bG6u
- Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013; 12: 822-838. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hZK6GF
- Baloh RW, Yue Q, Socotch TM, Jacobson KM. White matter lesions and disequilibrium in older people. I. Case-control comparison. Arch Neurol. 1995; 52: 970-974. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LcQnm3
- Ahmad H, Cerchiai N, Mancuso M, Casani AP, Bronstein AM. Are white matter abnormalities associated with "unexplained dizziness"?. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 358: 428-431. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Wt2Ehk
- Mattana P, Mannello F, Ferrari P, Augus GB. Vascular pathologies and inflammation: the anti-inflammatory properties of Sulodexide. J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012; 19: 1-7. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qJzAzo
- McGaugh JL. The amygdala modulates the consolidation of memories of emotionally arousing experiences. Annu Rev Neuroaci. 2004; 27: 1-28. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9RQcLA
- Fioresco SB, Tse MT. Dopaminerg regulation of inhibitory and excitatory transmission in the basolateral amygdala-prefrontal cortical pathway. J Neurosci. 2007; 27: 2045-2057. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wm4T9z
- Britton JC, Taylor SF, Sudheimer KD, Liberzon I. Facial expressionsand complex IAPS pictures: common and differential networks. Neuroimage. 2006; 31: 906-919. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uxJh88
- Doyère V, Debiec J, Monfils MH, Schafe GE, Le Doux JE. Synapse-specific reconsolidation of distinct fear memories in the latral amygdala. Nat Neurosci. 2007; 10: 4-6. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qBHEJ4
- Nader K, Schafe GE, Le Doux JE. Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval. Nature. 2000; 406: 722-726. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NDs91n
- Whalen PJ, Kagan J, Cook RG, Davis FC, Kim H, et al. Human amygdala responsivity to masked fearful eye whites. Science. 2004; 306: 2061. Ref.: https://goo.gl/sHPkvQ
- Kilts CD, Egan G, Gideon DA, Ely TD, Hoffman JM. Dissociable neural pathways are involved in the recognition of emotion in static and dynamic facial expressions. Neuroimage. 2003; 18: 156-168. Ref.: https://goo.gl/i95CLW
- Morrys JS, Friston Kj, Buchel C, Frith CD, Young AW, et al. A neuromodulatory role for the human amygdala in processing emotional facial expressions. Brain. 1998; 121: 47-57. Ref.: https://goo.gl/pGk9gK
- Kilts CD, Kelsey JE, Knight B, Ely TD, Bowman FD, et al. The neuronal correlates of social anxiety disorder and response to pharmacotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006; 31: 2243-2253. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eDs5jn
- Brandt T, Dieterich M. The vestibular cortex. Its locations, functions, and disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999; 871: 293-312. Ref.: https://goo.gl/njvVVz
- Marcelli V, Esposito F, Aragri A, Furia T, Riccardi P, et al. Spatio-temporal pattern of vestibular information processing after brief caloric stimulation. Eur J Radiol. 2009; 70: 312-316. Ref.: https://goo.gl/dK14o6
- Kim B, Kim JH, Kim MK, Lee KS, Kim Y, et al. Frontal white matter alterations in short-term medicated panic disorder patients without comorbid conditions: a diffusion tensor imaging study. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e95279. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LbpnNr
Figures:
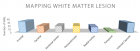
Figure 1
Similar Articles
-
Burnout and Related Factors in Caregivers of outpatients with SchizophreniaHatice Demirbas*,Erguvan Tugba Ozel Kizil. Burnout and Related Factors in Caregivers of outpatients with Schizophrenia. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hda.1001001; 1: 001-011
-
Anxiety and depression as an effect of birth order or being an only child: Results of an internet survey in Poland and GermanyJochen Hardt*,Lisa Weyer,Malgorzata Dragan,Wilfried Laubach. Anxiety and depression as an effect of birth order or being an only child: Results of an internet survey in Poland and Germany. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hda.1001003; 1: 015-022
-
Vestibular-limbic relationships: Brain mappingPaolo Gamba*. Vestibular-limbic relationships: Brain mapping. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001006; 2: 007-013
-
Responding to Disasters: More than economic and infrastructure interventionsDavid Crompton OAM*,Ross Young,Jane Shakespeare-Finch,Beverley Raphael AM. Responding to Disasters: More than economic and infrastructure interventions. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001007; 2: 014-028
-
Anti-anxiety effects in mice following acute administration of Ficus Thonningii (wild fig)Aduema W*,Akunneh-Wariso C,Ejiofo DC,Amah AK. Anti-anxiety effects in mice following acute administration of Ficus Thonningii (wild fig). . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001009; 2: 040-047
-
Translation, adaptation and validation of Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale in UrduWaqar Husain*,Amir Gulzar. Translation, adaptation and validation of Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale in Urdu. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001011; 4: 001-004
-
Depression as a civilization-deformed adaptation and defence mechanismBohdan Wasilewski*,Olha Yourtsenyuk,Eugene Egan. Depression as a civilization-deformed adaptation and defence mechanism. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001013; 4: 008-011
-
The different levels of depression and anxiety among Pakistani professionalsSehrish Hassan*,Waqar Husain. The different levels of depression and anxiety among Pakistani professionals. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001014; 4: 012-018
-
Impact of Christian meditation and biofeedback on the mental health of graduate students in seminary: A pilot studyPaul Ratanasiripong*,Sun Tsai . Impact of Christian meditation and biofeedback on the mental health of graduate students in seminary: A pilot study. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001015; 4: 019-024
-
Therapeutic application of herbal essential oil and its bioactive compounds as complementary and alternative medicine in cardiovascular-associated diseasesAhmad Firdaus B Lajis*,Noor Hanis Ismail. Therapeutic application of herbal essential oil and its bioactive compounds as complementary and alternative medicine in cardiovascular-associated diseases. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001016; 4: 025-036
Recently Viewed
-
Nanoencapsulated Extracts from Leaves of Bauhinia forficata Link: In vitro Antioxidant, Toxicogenetic, and Hypoglycemic Activity Effects in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic MiceBárbara Verônica Cardoso de Souza, Alessandra Braga Ribeiro*, Rita de Cássia Meneses Oliveira, Julianne Viana Freire Portela, Ana Amélia de Carvalho Melo Cavalcante, Esmeralda Maria Lustosa Barros, Luís Felipe Lima Matos, Tarsia Giabardo Alves, Maria. Nanoencapsulated Extracts from Leaves of Bauhinia forficata Link: In vitro Antioxidant, Toxicogenetic, and Hypoglycemic Activity Effects in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Mice. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001063; 8: 100-115
-
Oral Suspension as Versatile Galenic Formulation in PediatryMauro Luisetto*, Almukthar N, Edbey K, Mashori GR, Fiazza C, Dona’ l, Cabianca L, Latyshev O. Oral Suspension as Versatile Galenic Formulation in Pediatry. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001062; 8: 091-099
-
Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on DepressionKousik Maparu*. Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on Depression. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001061; 8: 089-090
-
Experiences of Consumers on the Health Effects of Fake and Adulterated Medicines in NigeriaChijioke M Ofomata, Nkiru N Ezeama, Chinelo Ezejiegu*. Experiences of Consumers on the Health Effects of Fake and Adulterated Medicines in Nigeria. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001059; 8: 075-081
-
Beta-1 Receptor (β1) in the Heart Specific Indicate to StereoselectivityRezk Rezk Ayyad*, Ahmed Mohamed Mansour, Ahmed Mohamed Nejm, Yasser Abdel Allem Hassan, Norhan Hassan Gabr, Ahmed Rezk Ayyad. Beta-1 Receptor (β1) in the Heart Specific Indicate to Stereoselectivity. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001060; 8: 082-088
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."